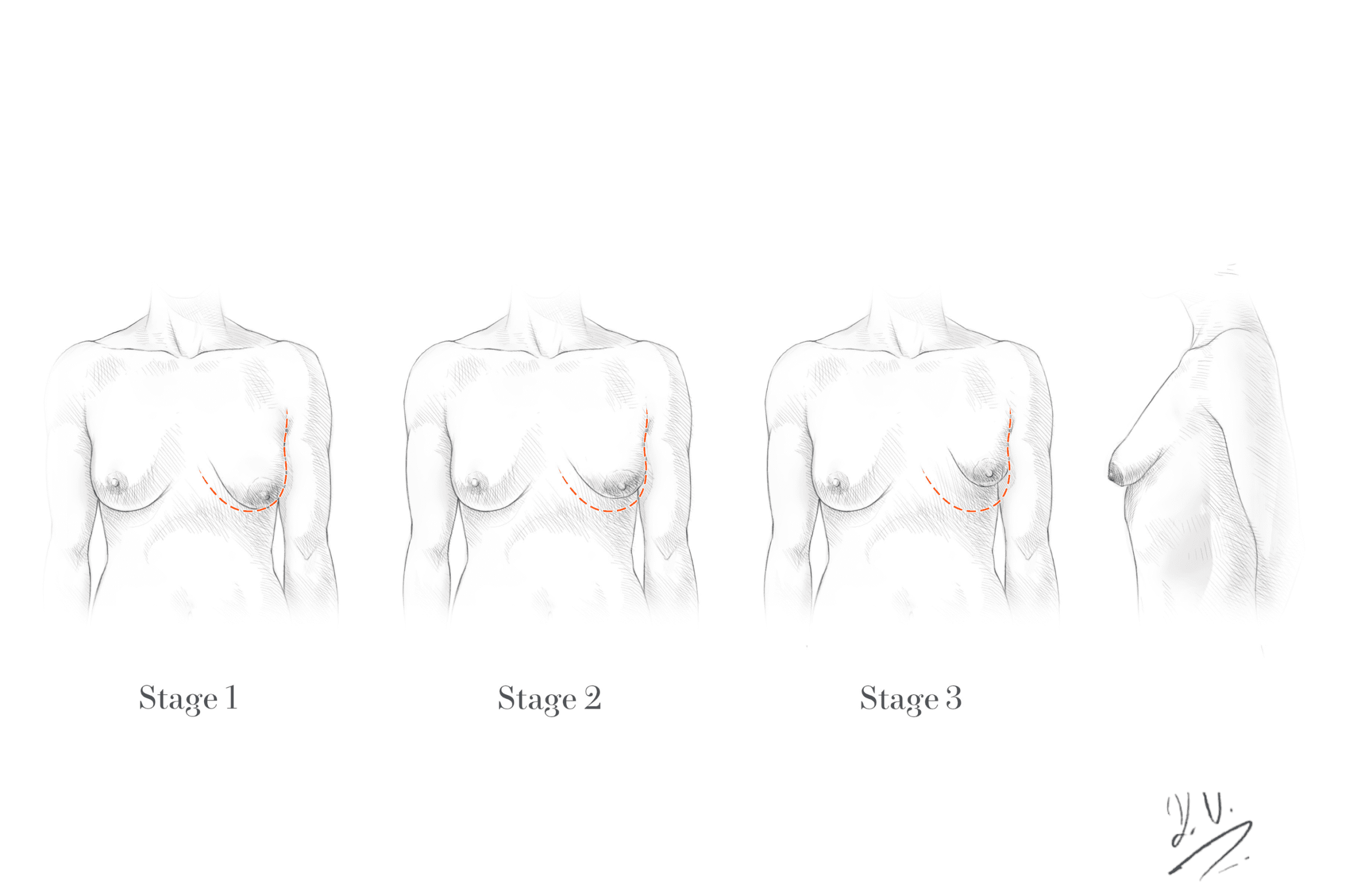
Tubular Breast: Anatomy, Challenges, and Treatment Options
Tubular breast is one of the congenital breast malformations that become visible during puberty and often cause significant psychological distress for affected women. This breast shape is characterized by a limited development of the breast base, resulting in an elongated, tube-like appearance. Frequently, the areola also appears disproportionately large. The severity can vary from very mild to pronounced, and often only one breast is affected or both sides to different degrees. Many women live for years with the feeling that their breast shape is not “normal,” without knowing that it is a medically recognized condition. Modern plastic surgery today offers various options to correct this anatomical variation and create a natural, harmonious breast shape.
What is meant by a tubular breast?
A tubular breast is a congenital malformation in which the breast tissue does not fully develop during growth. The term is derived from the Latin word for “tube” and describes the characteristic elongated shape of this breast anomaly. In contrast to a normally developed breast, which has a broad base, the tubular breast shows restricted horizontal expansion.
Anatomical characteristics of the breast shape
In a tubular breast, the connective tissue in the lower part of the breast is overly tight. This firm tissue functions like a ring that restricts the natural expansion of the mammary gland. The most important anatomical characteristics include:
- A significantly narrowed breast base with reduced horizontal expansion
- Tight connective tissue structures that encircle the mammary gland like a ring
- Preferential forward and downward growth of breast tissue instead of an even distribution
- A sudden transition between breast and chest wall without natural curvature
As a result, the breast tissue grows in an unnatural direction. This leads to a narrow breast base and frequently a conical or tube-like appearance.
Distinguishing from other breast malformations
Tubular breast is clearly distinct from other breast anomalies such as Poland syndrome-associated breast underdevelopment or simple breast asymmetry. While Poland syndrome also involves missing muscle tissue, tubular breast primarily affects the shape of the mammary gland. A precise diagnosis is crucial for selecting the appropriate treatment method.
How Does Tubular Breast Develop?
The exact development of this breast malformation has not yet been fully clarified scientifically. It is assumed that genetic factors and developmental biological processes during puberty interact. It is considered a variant of breast development that is determined by predisposition.
Developmental Causes
During pubertal breast development, connective tissue plays a central role. In women with tubular breasts, the so-called superficial fascia — a layer of connective tissue — is overly pronounced in the lower breast area. This fascia encloses the mammary gland like a ring and prevents its normal expansion downward and to the sides. Instead, the growing glandular tissue is pushed in a specific direction, resulting in the characteristic shape.
Why the Breast Shape Is Determined During Puberty
The critical phase for breast development occurs during puberty, when glandular tissue begins to grow under hormonal influence. The tubular shape manifests already at this early stage, as the anatomical restrictions are present from the beginning. Later hormonal changes such as pregnancy may further influence breast shape but no longer alter the underlying anatomy.
Typical Characteristics of a Tubular Breast
The characteristics can vary significantly between individuals. The most common features can be summarized as follows:
- Significantly narrowed breast base with reduced horizontal diameter
- Prominent or enlarged areola that often protrudes forward
- Elongated, tubular, or conical breast shape
- Increased distance between the two breasts
- Pronounced asymmetry between left and right sides
- Reduced lateral projection of glandular tissue
Thorough analysis of these features is essential for planning corrective treatment.
Narrowed Breast Base
The most striking feature is the clearly reduced breast base. While in a normally developed breast the diameter of the base roughly corresponds to the diameter of the anterior projection, in tubular breasts the base is often only half as wide. The breast appears narrow and elongated.
Prominent Areola
Another typical sign is an oversized or protruding areola. Due to pressure from the breast tissue, the areola often bulges forward. It appears elevated and clearly stands out from the rest of the breast tissue. Additionally, the diameter of the areola may be enlarged.
Asymmetries and Volume Deficits
Often both breasts are affected to different degrees, leading to pronounced asymmetry. One side may be almost normally developed while the other shows the classic characteristics. Volume is also frequently reduced, although some patients have sufficient glandular tissue that is simply compressed into an unfavorable shape.
Psychological and Aesthetic Challenges
For many affected women, tubular breast represents a significant burden. While the malformation usually does not cause functional impairments from a medical standpoint, the psychological component should not be underestimated.
Body Perception and Self-Image
Many affected individuals notice already during adolescence that their breasts develop differently from those of their peers. This can lead to a negative body image and low self-esteem. Situations such as changing rooms, swimming pools, or intimate moments are experienced as distressing. Some women develop avoidance strategies and exclusively wear clothing that conceals the chest.
Why Many Seek Help Late
Despite the high level of emotional distress, many women hesitate for a long time before seeking professional help. The reasons for this are varied:
- Lack of awareness that it is a medically recognized malformation
- Shame about discussing the topic
- Lack of knowledge about treatment options
- Concern about the risks of surgical intervention
- Uncertainty regarding the outcome
Often, the emotional distress is suppressed for years. However, early counseling would be valuable in order to develop realistic expectations.
Diagnosis of Tubular Breast
Diagnosis is made through a comprehensive clinical examination. An experienced plastic surgeon can identify the characteristic features and assess the severity.
Clinical Assessment and Individual Analysis
During the examination, various parameters are systematically evaluated:
- Width and shape of the breast base
- Height and position of the inframammary fold
- Size, shape, and projection of the areola
- Degree of asymmetry between both sides
- Quantity and distribution of existing breast tissue
- Skin quality and tissue elasticity
- Position of the nipple in relation to the breast fold
This detailed analysis forms the basis for developing an individualized treatment plan.
Importance of Precise Planning
Correcting a tubular breast requires more than a standard breast augmentation. The anatomical characteristics must be specifically addressed to achieve a harmonious result. For this reason, preoperative planning is crucial. Modern methods can help visualize the intended outcome.
Treatment Options for Tubular Breast
Correction requires a multi-step surgical approach. The goal is to eliminate anatomical restrictions and create a natural-looking breast shape.
Surgical Correction of Breast Shape
Surgery for tubular breast consists of several components that are individually combined depending on the severity. The essential surgical steps include:
- Releasing the tight connective tissue structures through precise incisions
- Mobilizing and repositioning the breast tissue
- Expanding the breast base downward and laterally
- Shaping the breast for a natural round appearance
- Adjusting the inframammary fold and the areola
- Stabilizing the new shape through suturing or implant techniques
The central element is the incision of the constricting tissue, which allows the mammary gland to distribute more evenly.
Expansion of the Breast Base
A key step in correcting tubular breast is increasing the width of the breast base. For this purpose, the tissue in the lower and lateral areas is mobilized and repositioned. The tight fascia is incised to create space for expansion. In some cases, the inframammary fold is lowered to allow more vertical projection.
Adjustment of the Areola
A protruding or enlarged areola often requires correction. Excess tissue is removed and the areola is reduced in size. The technique must preserve sensitivity and breastfeeding capability as much as possible.
Volume Enhancement and Shape Correction
In most cases, additional volume enhancement is necessary to achieve the desired shape. This may be done using implants or autologous fat. The implant not only increases volume but also helps stabilize the corrected shape.
Breast Augmentation in Tubular Breasts
Most corrective procedures involve augmentation with implants. However, this differs from a standard breast augmentation. Selecting the appropriate implant is complex. Shape, size, and projection must be precisely tailored to the individual anatomical conditions. Round implants with high projection are often used. Placement is typically submuscular, as this provides additional coverage.
Combination With Shape-Correcting Techniques
Implant placement alone would not correct the tubular shape. Therefore, augmentation is always combined with the shape-correcting measures described above. Only after releasing the constricting structures can the implant create a natural breast shape.
Breast Lift in Tubular Breasts
In some cases, a lift is required in addition to shape correction, especially when excess skin is present. A breast lift is considered when the nipple sits very low or when additional skin excess has developed after pregnancies. The lift removes excess skin and elevates the nipple to an aesthetically pleasing position.
Harmonizing Shape and Proportion
The goal in treating tubular breasts is an overall result in which breast shape, volume, and position are in harmony. Incision and scar placement are chosen to be as discreet as possible. Modern techniques allow scars to be placed around the areola, where they become barely visible after healing.
Individual Treatment Approach at Dr. Kelly®
Every tubular breast manifests differently. At Dr. Kelly®, great emphasis is placed on a tailored treatment plan that matches the patient’s unique anatomy. The team develops an individualized surgical concept for each patient, taking all relevant factors into account: the severity of the malformation, skin quality, existing breast volume, and aesthetic goals.
Natural Results and Medical Safety
Dr. Kelly®’s many years of experience in breast surgery allow even complex cases to be planned with precision. The objective is to create a breast shape that looks harmonious and natural, optimizing the patient’s individual anatomy. Safety and health always come first. All procedures are carried out according to the highest medical standards.
Treatment Process
Correction of tubular breasts is a multi-step process that begins with a detailed consultation and includes close postoperative follow-up. During the initial consultation, the breast anatomy is carefully analyzed and the various treatment options are discussed. It is important that patients receive a realistic understanding of what can be achieved.
Surgery and Inpatient Care
Prior to surgery, medical pre-assessments are carried out. Planning also includes selecting the implants and defining the exact surgical approach. The procedure is performed under general anesthesia and takes between two and four hours, depending on complexity. After surgery, the patient remains in the clinic for monitoring. Depending on individual recovery, an overnight stay may be advisable.
Aftercare and Healing Process
The period following surgery is crucial for the final outcome. Consistent aftercare supports healing and minimizes risks. In the first few days, swelling and a feeling of tightness can be expected. For optimal healing, patients should follow these guidelines:
- Consistently wear a special support bra for at least six weeks
- Avoid heavy lifting and strenuous activities during the first three weeks
- Sleep in an elevated position during the first week
- Avoid sports and exercise for at least four to six weeks
- Protect scars and avoid direct sun exposure
Swelling gradually decreases over time, and the final result becomes fully visible only after several months.
Long-Term Stability of Results
The corrected breast shape is generally stable long-term. The released anatomical restrictions do not recur, and the implant provides lasting shape support. Naturally, the breast is still subject to normal aging processes. However, the fundamental improvement in breast shape remains.
Realistic Expectations for the Result
Open communication about the possibilities and limits of treatment is essential for patient satisfaction. Modern surgical techniques make it possible to significantly improve even pronounced tubular breasts. The narrowed base can be widened, the areola adjusted, and a harmonious shape created. In many cases, the result is so convincing that the original malformation is no longer recognizable.
Transparent Discussion of Limitations
Not every asymmetry can be completely eliminated, and minimal scarring is unavoidable. Nipple sensitivity may also be temporarily reduced. Absolute perfection is not medically achievable. It is important that patients understand these realities while still being able to expect a significant improvement.
Personal Consultation at Dr. Kelly®
The first step toward potential treatment is always a personal consultation. During this appointment, all questions can be addressed, the individual situation analyzed, and a tailored treatment plan developed. The team takes time to address concerns and determine the best path forward together.